Tuberculosis (TB): Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Risk Factors
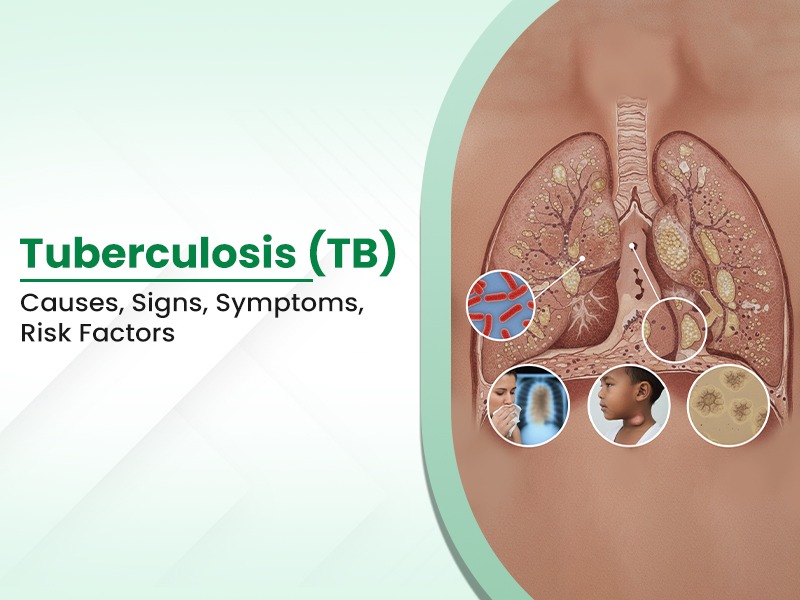
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious and potentially life-threatening infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs. It is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads from person to person through airborne droplets. When TB involves the lungs, it becomes highly infectious and requires immediate medical attention from a pulmonologist in Indirapuram.
In this blog, we discuss the causes, signs and symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and treatment options for tuberculosis.
What is TB (Tuberculosis)? Their Types
Tuberculosis is a serious bacterial infection that mainly affects the lungs but can also involve other organs. Here are the most common types of tuberculosis (TB):
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common type, where the lungs become infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis: Extrapulmonary tuberculosis affects organs outside the lungs, such as lymph nodes, joints, bones, kidneys, and brain.
- Latent Tuberculosis: Latent tuberculosis affects inactive tuberculosis bacteria in the body without symptoms. It’s not contagious. This means you can’t pass the disease on to others.
- Active Tuberculosis: In active tuberculosis, bacteria are actively multiplying and causing symptoms and illness.
- Drug-resistant Tuberculosis: Drug-resistant tuberculosis includes RR-TB, MDR-TB, and XDR-TB, with MDR-TB and XDR-TB being particularly serious forms of tuberculosis.
Signs & Symptoms of Tuberculosis (TB)
TB symptoms vary based on the organ involved and disease activity.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis (By Type)
Types of Tuberculosis and Their Symptoms
Latent Tuberculosis
-
No visible symptoms
-
Not contagious
-
Can reactivate if immunity weakens
Pulmonary Tuberculosis (Lung TB)
-
Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
-
Blood or mucus in sputum
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fever and night sweats
Active Tuberculosis (General Symptoms)
-
Persistent fever
-
Severe fatigue and weakness
-
Unintentional weight loss
-
Loss of appetite
-
Chills
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
-
Persistent symptoms despite treatment
-
Worsening cough or fever
-
Prolonged or recurring illness
Symptoms of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis (By Organ Involved)
Lymph Nodes
-
Painless swelling, most commonly in the neck
Bones & Joints
-
Stiffness
-
Reduced movement
Brain (TB Meningitis)
-
Headache
-
Vomiting
-
Confusion
-
Seizures
Kidneys
-
Flank or lower back pain
Abdomen
-
Abdominal pain
-
Bloating
-
Bowel disturbances
Skin
-
Slow-healing ulcers
-
Nodules
Why Does TB Occur?
Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Once it enters the body, it can stay inactive or spread through the bloodstream to affect different organs. Here’s how TB infection occurs across types:
Pulmonary TB
-
Develops when TB bacteria settle in the lungs after inhalation
Extrapulmonary TB
-
Occurs when TB bacteria spread from the lungs to other organs through the blood or lymphatic system
Latent TB
-
The immune system controls the bacteria, preventing active disease and symptoms
Active TB
-
Develops when the immune system fails to contain the bacteria, leading to illness
Drug-Resistant TB
-
Develops due to incomplete, irregular, or improper TB treatment
TB does not spread through touching, sharing food, or casual contact. It spreads only by inhaling infected droplets, especially during prolonged exposure.
Risk Factors of TB
There are many risk factors for developing tuberculosis, as suggested by the doctors from the best hospital in Ghaziabad, including:
- Close or prolonged contact with an active TB patient
- HIV/AIDS or weakened immunity
- Diabetes
- Cancer or immunosuppressive therapies
- Malnutrition and low body weight
- Smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use
- Overcrowded living conditions and poor ventilation
What are the Right Treatment Options for TB?
TB treatment relies on the type of TB, the organs that are affected, and how well the drug works. If you start and complete the course early, you’ll be cured and avoid resistance. The general physician in Indirapuram chooses the schedule, taking into account the patient’s health status and the possibility of tuberculosis infection.
Treatment for Latent TB
Latent TB is treated to prevent future activation. Your physician will recommend the following medicines:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampicin
- Rifapentine
- Ethambutol (when required)
Treatment duration ranges from three to six months.
Standard First-Line Treatment Regimen for Drug-Susceptible Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Standard regimen of treatment at the leading hospitals in Ghaziabad consists of two phases:
Intensive Phase (2 months):
- Rifampicin (R)
- Isoniazid (H)
- Pyrazinamide (Z)
- Ethambutol (E)
Continuation Phase (4 months):
- Rifampicin (R)
- Isoniazid (H)
Treatment may be given daily or under DOT (Directly Observed Treatment) as advised by the physician.
Treatment for Extrapulmonary TB
Your physician will recommend the same medicines as for pulmonary TB. However, the duration will be extended to nine to twelve months for:
- TB meningitis
- Bone and joint TB
- Corticosteroids might also be added in selected cases (brain or pericardial TB)
Managing Drug-Resistant TB
Drug-resistant TB is more complex and needs specialised care. Doctors carefully select second-line medicines and closely monitor progress to reduce side effects and improve outcomes.
How to Prevent Tuberculosis?
As per the best pulmonologist in Indirapuram, you can reduce your risk of getting and spreading TB by:
- Washing hands frequently
- Covering mouth and nose while coughing or sneezing
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Completing prescribed TB medications
- Avoiding work or school until cleared by a healthcare provider
Cure Tuberculosis with Effective Treatment and Care!
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment play a crucial role in preventing complications and stopping the spread of tuberculosis. TB is a curable disease when treated correctly and completely.
At Yashoda Medicity, experienced pulmonologists and physicians provide comprehensive TB care using advanced diagnostics and evidence-based treatment protocols. A pulmonologist in Indirapuram will guide you through every stage of diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
FAQs
- What is tuberculosis (TB)?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and treatable serious bacterial infection, usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, that most commonly affects the lungs, but can affect any part of the body, including the kidneys, spine, and brain.
- How does TB spread?
Tuberculosis is spread by airborne bacteria from active patients during activities that require prolonged exposure, such as coughing or talking, but not through everyday contact, such as shaking hands or sharing food.
- What are the common symptoms of TB?
Common symptoms of tuberculosis (TB) include persistent cough (for more than 3 weeks), chest pain, hemoptysis/mucus, night sweats, fever, fatigue, chills, and severe unexplained weight loss with loss of appetite.
- Is TB curable?
Yes, tuberculosis (TB) is a treatable bacterial infection, but it requires continuous administration of certain antibiotics over a long period of time (usually for 6 months or more). Additionally, to prevent drug resistance and relapse, it is essential to complete all treatments, even if symptoms have improved.
- Can TB cause death?
Yes, tuberculosis (TB) can be fatal as it is a serious infection that affects the lungs and other parts of the body and can be fatal if not treated properly. Still, it can be cured with continued antibiotic treatment.

